
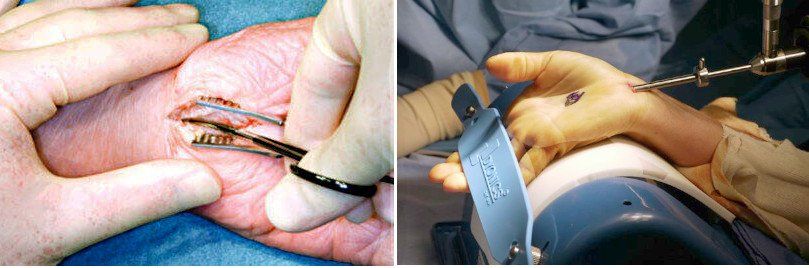
However, this type of surgery is not suitable for all people. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release usually has a quicker recovery time, produces less post-operative pain and causes less scaring than open release surgery. The procedure may be done endoscopically (where instruments are passed into the wrist through small incisions) or using the open technique (where a larger incision is made to enable access to the surgical area).īoth surgeries are normally performed on a day-stay basis and can usually be carried out using a local anaesthetic. It involves locating and cutting (releasing) ligaments around the carpal tunnel, relieving pressure on the median nerve. The surgery is commonly referred to as a carpal tunnel release. If non-surgical treatment is unsuccessful, surgery may be recommended. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or corticosteroids (eg: cortisone injections).Modifying how you do certain tasks or activities, or avoiding them altogether.Wearing a splint to support the wrist and prevent it moving into a position that further increases compression of the median nerve.Applying a cold pack to reduce swelling.Taking frequent breaks to rest the hands.Initial treatment will aim to reduce and manage symptoms without surgery. Treatment will depend on the nature and severity of the symptoms. MRI scans, x-rays and blood tests may be performed to rule out other possible causes for the symptoms, such as arthritis or a fracture. Ultrasound or MRI scans may be recommended in some cases to confirm compression of the median nerve. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be indicated if impulses along the median nerve are slowed in the carpal tunnel. These tests measure how quickly nerves can transmit electrical impulses. Diagnosisĭoctors can normally diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome based on a discussion about the nature and circumstances associated with the symptoms, a physical examination and nerve conduction tests. In the majority of cases the cause will be unknown. Currently, there is no conclusive evidence to link keyboard and computer work with the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. The risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome can be increased by activities or occupations that involve prolonged and highly repetitious movements of the wrist, especially when a forceful grip is required. Pregnancy and menopause (fluid retention may increase pressure within the carpal tunnel).A wrist injury such as a fracture or dislocation.Certain conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, underactive thyroid and obesity.When the tissues in the carpal tunnel become swollen, the median nerve becomes compressed or “entrapped”.įactors that increase the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome include:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
